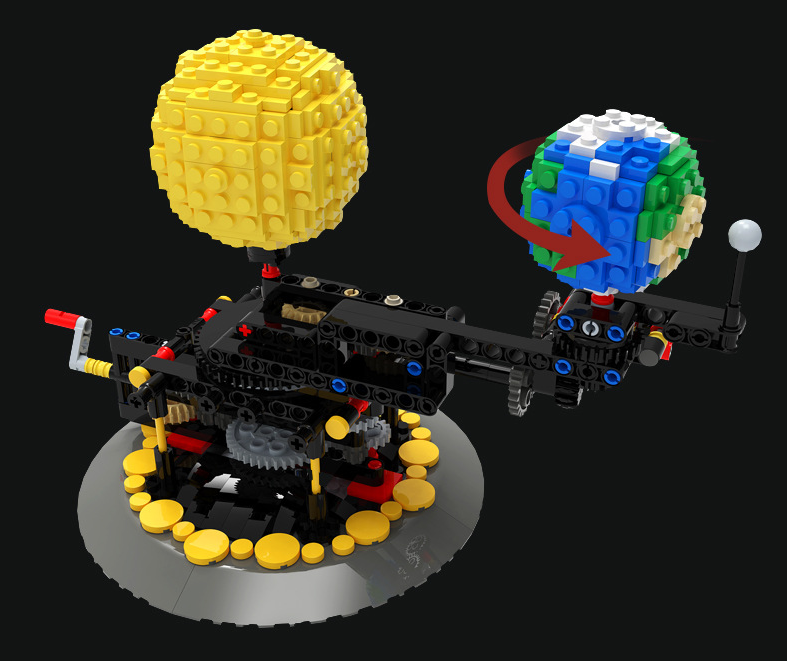
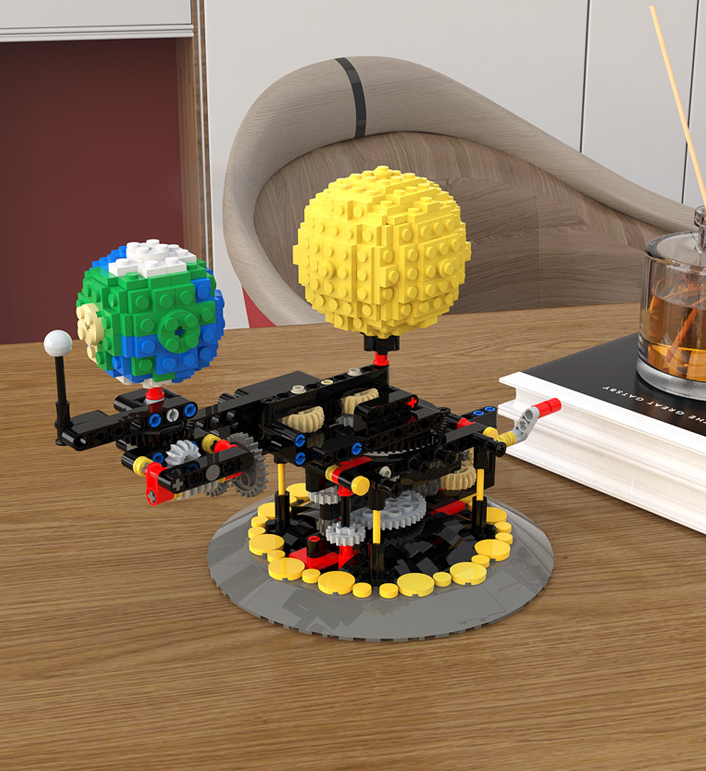





Simulate The Rotation Of Moon Earth And Sun
$103.99 NZD
To simulate the rotation and interaction of the Moon, Earth, and Sun, you can use a model or visualization that demonstrates:
- Earth’s Rotation: The Earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours.
- Earth’s Revolution Around the Sun: The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365.25 days.
- Moon’s Revolution Around Earth: The Moon orbits Earth roughly every 27.3 days.
Here’s a breakdown of how to simulate their motion effectively:
Materials for a Physical Model
- A large light source (e.g., a lamp) to represent the Sun.
- A globe or ball to represent the Earth.
- A smaller ball (e.g., a ping pong ball) to represent the Moon.
- Strings or stands to hold the Earth and Moon in position relative to the Sun.
- Dark room for a better visual of shadows and light dynamics.
Steps to Simulate
-
Set up the Sun:
- Place the lamp in a fixed position to act as the Sun, emitting light in all directions.
-
Show Earth’s Rotation:
- Place the Earth ball on a stand or axis, tilted approximately 23.5°.
- Rotate the Earth ball counterclockwise (when viewed from above the North Pole) to show its daily rotation.
-
Add the Moon’s Orbit:
- Attach the Moon ball to a string or orbiting arm around the Earth ball.
- Move the Moon counterclockwise around the Earth to simulate its monthly orbit.
- Note that the Moon always keeps the same face toward Earth (tidal locking).
-
Demonstrate Earth’s Orbit Around the Sun:
- Place the Earth (with Moon in orbit) on a larger circular path around the lamp.
- Move the Earth counterclockwise to simulate its annual orbit.
-
Explain Shadows and Eclipses:
- Show how the Moon’s position relative to the Earth and Sun causes phases of the Moon, solar eclipses, and lunar eclipses.
- Align the Moon, Earth, and Sun to demonstrate these phenomena.
Digital Simulations
If you prefer a digital visualization, you can use tools or simulations such as:
- Stellarium (Astronomy Software): Allows you to explore real-time orbits and motions.
- NASA's Eyes on the Solar System: Interactive web tool to visualize celestial dynamics.
- 3D Simulations in educational apps like Universe Sandbox or interactive animations on educational websites.
Key Points to Explain During Simulation
-
Earth’s Day/Night Cycle:
- Caused by Earth’s rotation on its axis.
-
Seasons:
- Result from Earth’s tilted axis as it orbits the Sun.
-
Phases of the Moon:
- Occur as the Moon orbits Earth, showing varying portions of its sunlit side.
-
Eclipses:
- Solar Eclipse: When the Moon blocks sunlight to Earth.
- Lunar Eclipse: When Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon.
Product information:
Material: Plastic/Plastic
Plastic material classification: ABS
Plastic building block type: small particles
Block net weight: 0.5676kg
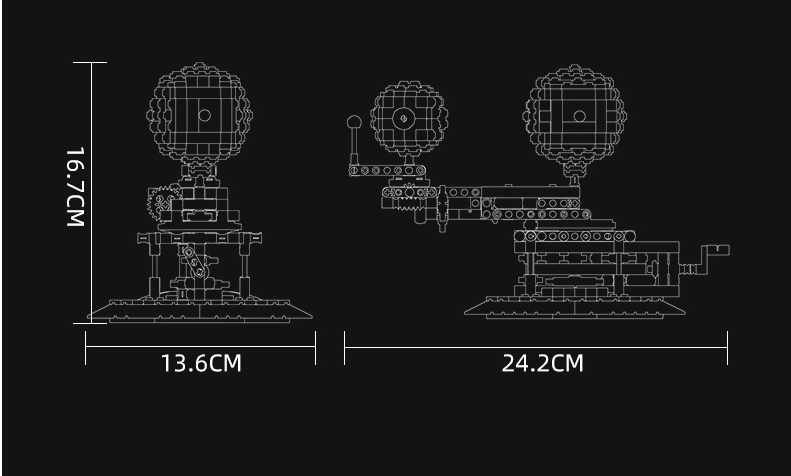
Size: 24.2*16.7*13.6cm
Packing list:
Building block*461
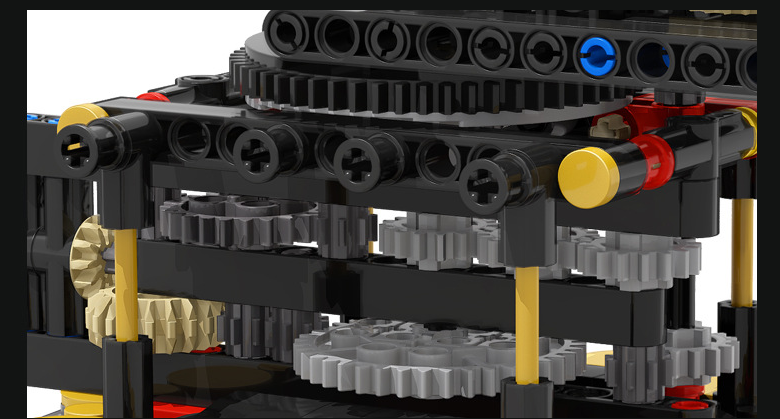
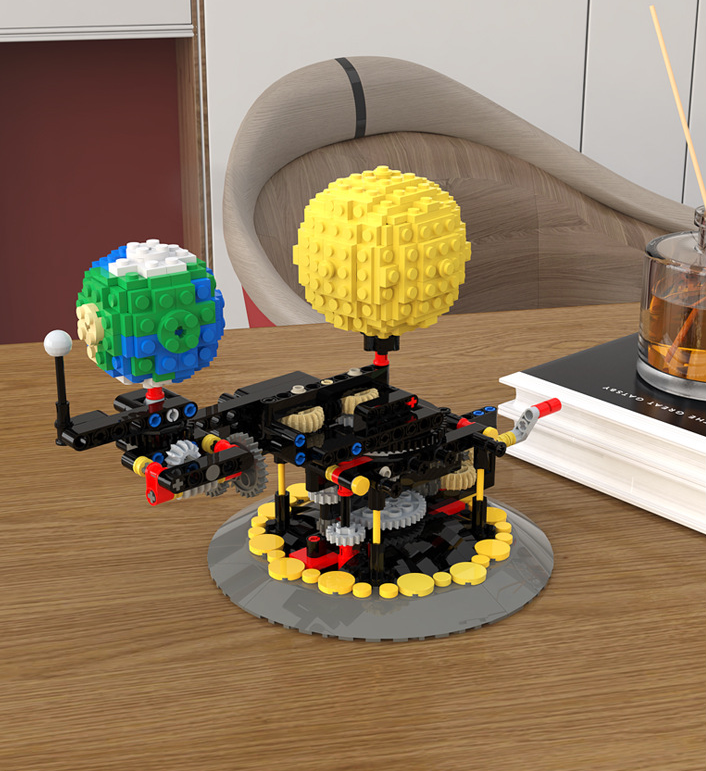
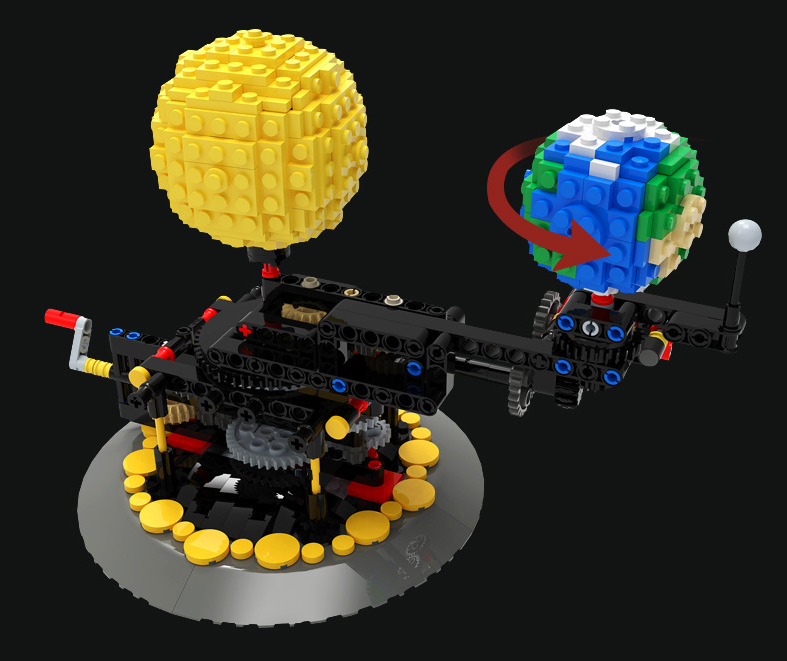
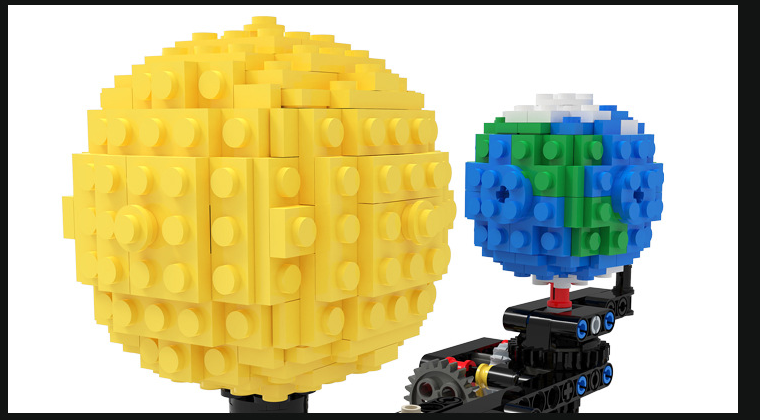







The product may be provided by a different brand of comparable quality.
The actual product may vary slightly from the image shown.
Shop amazing plants at The Node – a top destination for plant lovers



















.jpg)









.jpg)





.jpeg)





.jpeg)



.jpeg)








.jpeg)



.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.jpeg)




.jpeg)
.jpg)

.jpeg)






.jpeg)
.jpeg)




.jpeg)





.jpeg)


.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.jpeg)

.jpeg)







.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)





.jpeg)



.jpeg)






.jpg)
.jpeg)









.jpg)


ulva-Logo.jpg)




.jpeg)



.png)















.png)
























